“Break the Crypto onion: Layer 1 to Layer Solution 3 and the consequences of” Rekt “”
As the space for cryptocurrencies continues to grow in popularity and adoption, concerns have been set up due to risk and vulnerability inherent blockchain technology. Among the most controversial issues are the solutions of the layer 1 (L1), which provide the basis for the entire ecosystems and protocols of the layers 2 (L2), which offer faster time of transaction processing, but come with their own problems.
Layer 1 Solution: The foundation of all
Layer 1 solution, also known as the “backbone” or “mainnet”, relate to the underlying infrastructure, which enables the entire network of cryptocurrencies. These solutions are responsible for confirming transactions, creating new units (eg tokens) and ensuring blockchain integrity. Some distinguished solutions L1 include:
- Ethereum (ETH): The largest and most commonly used blockchain platform, with over 120 million registered users.
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most famous cryptocurrency, which has a market capitalization of over $ 500 billion.
- Cardano (ADA): Decision for proof (POS) L1 that aims to improve scalability and security.
Risks of layer solutions 1
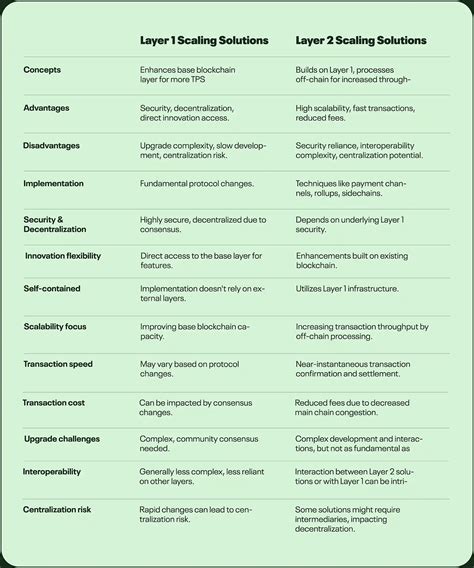
While L1 solutions provide the basis for whole ecosystems, they also have significant risks. One of the most significant concerns is the potential for centralization, where one entity controls most of the network blocks or has the ability to manipulate transactions. In addition, L1 solutions are often sensitive to hacking and security violation, which may have pernicious consequences for users.
Layer 2 Solutions: Faster, cheaper alternative
In response to risks associated with layer 1 solutions, the developers turned to the layer 2 (L2) protocols as faster, cheaper alternatives. L2 solutions operate at the top of the basic blockchain and offer improved scalability, reduced latency and increased safety. Some popular L2 solutions include:
- Optimism (OPT): Decision for proof (POS) L2 that uses transactions outside the chain to reduce fees.
- Polygon (Matic): Blockchain platform that enables developers to build decentralized applications (DAPPS) using Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
- Cosmos (atom): a multi -stroke frame that allows the creation of independent blockchain, each with its own scalability and security features.
Problem “Rect”
Unfortunately, some developers have become a victim of phenomenon known as “Rect”, where they take over excessive debt or collateral to support their L2 projects. These persons often become trapped in the borrowing, consumption and accumulation cycle, which ultimately leads to financial downfall.
Conclusion
As the space for cryptocurrencies continues to develop and mature, developers are crucial to understand the risks and consequences associated with the solutions of layer 1 and L2 protocols. Although these alternatives offer faster, cheaper and safer options, they also require a deep understanding of blockchain technology and its basic mechanics.
Ultimately, the fate of each L1 solution or L2 protocol is determined by its ability to provide values to users with risk minimization. As the crypto landscape continues to take place, it is crucial for developers and investors a priority to priority caution, research and attention when exploring these emerging technologies.
A statement of the renunciation of responsibility: This article is only for informative purposes and should not be considered as an investment advice. Crypto currencies are known for its high volatility and may result in significant losses if they are not managed properly.
Leave a Reply